Researchers at the UPV/EHU and the BioCruces-Bizkaia Institute of Healthcare Research (IIS) have recently published an article in the Human Molecular Genetics journal in which they report on the discovery of a biomarker that could enable celiac disease to be diagnosed in the blood of people on a gluten-free diet. The UPV/EHU has patented this discovery so that in the future it can be transferred to companies interested in marketing this new diagnostic system.
The UPV/EHU-University of the Basque Country patents a biomarker for diagnosing celiac disease in the blood of people who do not consume any gluten
A biomarker for diagnosing celiac disease in people on a gluten-free diet
- Research
First publication date: 30/05/2019

Celiac disease is a complex condition, routinely treated by means of a strict gluten-free diet. One of the diagnostic challenges of this disease is that patients need to be consuming gluten so that a correct diagnosis by means of endoscopy can be made. Yet nowadays there are more and more people who opt to eliminate gluten from their diets before seeing a specialist, and this makes it tremendously difficult to reliably diagnose the disease. However, as José Ramón Bilbao and Nora Fernandez-Jimenez, researchers at the UPV/EHU and the Biocruces-Bizkaia Institute of Healthcare Research, pointed out, “the self-diagnosis of gluten intolerance is a growing global phenomenon as it reaches 12-13 % of the general population in European countries such as Italy and the United Kingdom”.
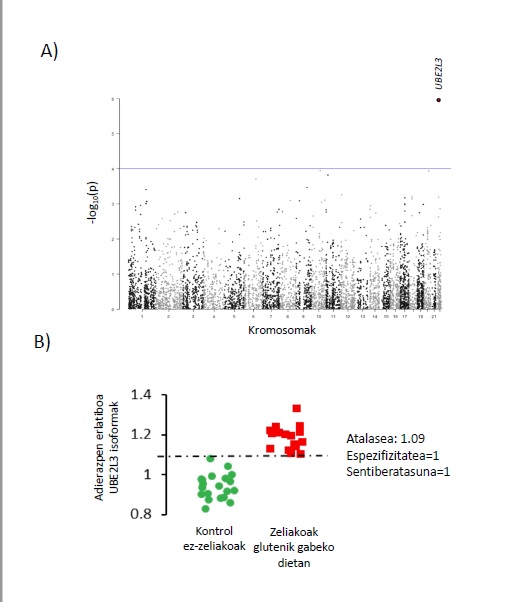
In an article published recently in the Human Molecular Genetics journal these researchers report on the discovery of a biomarker that could enable celiac disease to be diagnosed in the blood of people on a gluten-free diet. In this work, though an analysis of applied statistics, the researchers have discovered that the relative expression of the isoforms of the UBE2L3 gene in the blood makes it possible to distinguish with 100 % sensitivity and specificity celiac patients on a gluten-free diet.
From basic research to clinical practice
The UPV/EHU has patented this discovery so that in the future it can be transferred to companies interested in marketing this new diagnostic system. Right now, Dr Fernandez is focussing her efforts on securing funding because “last year the project received an award for best poster at the Congress of the Spanish Celiac Disease Society, but now further funding needs to be secured to validate the biomarker in a larger cohort of people”. According to Dr Bilbao, “UBE2L3 is an example of how the transfer from basic Genomics research to clinical practice is possible, and could have a huge impact on the routine diagnosis of celiac disease”.
Additional information
The PhD holder in Biology José Ramón Bilbao-Catalá is an adjunct professor in the Department of Genetics, Physical Anthropology and Animal Physiology of the UPV/EHU's Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, lead researcher in the Functional Celiac Disease group, and coordinator of the Endocrinology, Metabolism, Nutrition and Kidney Disease research area at the BioCruces-Bizkaia IIS.
Following a post-doctoral stay at the WHO International Agency of Cancer Research in France, Dr Nora Fernandez-Jimenez currently works at the BioCruces-Bizkaia IIS. She is a post-doctoral researcher in the Genomics and Epigenomics of complex diseases and normal child development.
Bibliographical reference
Nora Fernandez-Jimenez, José Ramón Bilbao
Mendelian Randomization analysis of celiac GWAS reveals a blood expression signature with diagnostic potential in absence of gluten consumption
Human Molecular Genetics, 2019
DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddz113